
The first generation of tango musicians are commonly referred to as "La Guardia Vieja" (The Old Guard). The first Period of "La Guardia Vieja" lasted from approximately 1895 to 1910. These songs are a type of habanera blended with African and European music and are sometimes referred to as "tango-habanera," "tango criollo" or "tango-milonga."
This period saw:
- Tango being born from local, habanera, African and European influences
- Formations of musical trios
- The introduction of the bandoneon
- A formal structure for Tango emerging
- Academias y Cabarets and other public dance spaces opening
- Men learning with other men
- Tango travelling to Europe
- The introduction of recorded tango.
The music originated in the "Rioplatenese" or Río de la Plata region of Argentina and Uruguay. Some of the origins of the music would be candombe, vals criollo, habanera, flamenco, polka, milonga (different from the milonga we know today and was a type of "battle" poetry), mazurka and contradanse. In essence, you had European immigrants with their instruments being influenced heavily by Latin American and African music.
It is true that only about 8,000 black argentines existed out of a population of over 400,000 in 1887, but all it took was a few to have a great impact on tango. The best example of this was Leopoldo Ruperto Thompson. Get this, he was a bass player who played with Firpo, Canaro, Arolas, de Caro and Cobián. Many of the first bandoneon players and guitarists were black. Also, some of the earliest composers of tango including Mendizábal and Carlos Posadas, as well as many of the earliest dancers and teachers.
At this time Tango was played by solo guitar or piano, small ensembles (conjuntos) and municipal marching bands. The ensembles were usually trios and would often consist of some combination of flute, clarinet, guitar and/or violin. The guitar would often play the habanera rhythm while the flute, clarinet and/or vilolin played the melody. Sometimes, these groups would be accompanied by male or female singers. They would play in cafés, beer houses, courtyards of conventillos (poor apartment houses) and also in brothels. The music would also have been played around the city by organitos or organ-grinders who went around the city playing portable player-organs.
Towards the end of this period we also saw the signature instrument of tango, the bandoneon, introduced to the ensembles. The bandoneon was a concertina type of instrument created in Germany for churches that could not afford an expensive organ. It made its way over to Argentina and Uruguay with the huge influx of immigrants.
 |
 |
During this time, tango begins to take on structure. In 1897, Anselmo Rosendo Menizábal composed, "El entrerriano (The Man from Between the Rivers)" which was the first tango structured in three distinct sections. The 1st and 3rd sections had 16 measures and the 2nd measure had thirty-two measures.
 In the early 1900s, many academias and cabarets began to open around the city. Academias were places were people could learn the choreography of tango and other dances. Cabarets were public places where people could dance and play tango. Armenonville, at the corner of Avenida Alvear y Table, was one of the first of these places. Other establishments were also opening and promoting tango like Hansens which was a restaurant/café on Avenida Sarmientos. The picture on the left was taken in March of 1905 at a carnival at the Pabellón de las Rosas (Rose Pavillion), a popular dance venue in Buenos Aires.
In the early 1900s, many academias and cabarets began to open around the city. Academias were places were people could learn the choreography of tango and other dances. Cabarets were public places where people could dance and play tango. Armenonville, at the corner of Avenida Alvear y Table, was one of the first of these places. Other establishments were also opening and promoting tango like Hansens which was a restaurant/café on Avenida Sarmientos. The picture on the left was taken in March of 1905 at a carnival at the Pabellón de las Rosas (Rose Pavillion), a popular dance venue in Buenos Aires.
This period also saw men dancing with other men. The primary reasons for this was that men greatly outnumbered women and so the women had their pick of the men to dance with. So, the men would get together and practice and learn from one another in order to improve so that the could attract the few women dancers. This was a time when women and men could not associate as easily as today.
.jpg)
Many early pioneers of rioplatense tango travelled to Europe including Angel Villoldo, Alfredo Gobbi, and his wife, Flora Hortensia Rodriguez to record ind France and Germany. Below are some of the earliest recordings of tango. These recordings are from vinyl LPs and 78s. I am working on getting them all recorded and posting as much historical information about them as possible.
Between 1906 and 1910, 850,000 immigrants arrived in Buenos Aires and the population grew to 1,500,000, setting the stage for the next period of tango's growth.
 “La Morocha” (?)
“La Morocha” (?)
Composer: Enrique Saborido
Performed by: Recording of an orginal Barrel Organ (Organito)
The original sheet music describes the song as "tango criollo." There is some debate about whether or not this or "el choclo" was the first tango to be exported to Europe. Saborido travelled to Paris and was there in 1911 teaching people how to play and dance tango. Of course, this version is an instrumental, but Angel Villoldo did add lyrics to the song.
More on Enrique Saborido: http://www.todotango.com/
More on "La Morocha:" http://www.todotango.com/
"El Sargento Cabral" (1907)
Composer: Manuel O. Campoamor
Performed by: Banda de la Guardia Republicana de Paris
.gif)
The pianist and composer Manuel O. Campoamor numbered all his tangos and "El Sargento Cabral", dating from 1898 or 1899 is number 1.
Campoamor was born on November 7, 1877 in Montevideo, Uruguay, but he grew up in Buenos Aires, Argentina. He learned to play the piano by ear and never learned to write music. He composed tangos from 1898 to 1905 and kept playing piano publicly until 1922, but according to his wife he would still play at home every day until his death in 1941 of Lung Cancer. He is quoted as saying, "I didn't compose any more and don't even think of doing it; I neither have the enthusiasm nor the time to devote to that. Today the output is overwhelming and the number of composers is great. The present generation has adopted a different beat for tango, which is warmly welcome by the public; we, those who feel tango in quite a different way, have to withdraw to allow the new trends to express this new sensitivity."
"El Sargento Cabral" was published in 1899 by Gath & Chaves house where Campoamor worked for 25 years, eventually becoming manager.
It was edited by J. A. Medina e Hijo and it as dedicated to the composer Leopoldo Corretjer. According to the author, this work owes its title to a common occurrence in local dance spots of the time. Following a competition someone from the winning side would exclaim, "We have beat the enemy!" in parody of what Sargent Cabral said shortly before his own death in the battle of San Lorenzo.
The recording of Paris' Republican Band belongs to a series of recordings made specifically for the recording house, Gath & Chaves. They sent several pioneers of rioplatense tango to Europe including Angel Villoldo, Alfredo Gobbi, and his wife, Flora Hortensia Rodriguez to record because there was no recording studio in Buenos Aires.
Campoamor also worked as a pianist in the famous house of Maria "La Vasca" which can still be found at the corner of Carlos Calvo Street and Jujuy Street.
For more information on Campoamor visit: http://www.todotango.com/
 "Mordeme la oreja izquierda" (Bite my left ear) (1908)
"Mordeme la oreja izquierda" (Bite my left ear) (1908)
Composer: Eugenio M. de Alarcon
Performed by Banda Española
This edition of the tango dates from 1906 and belongs to the composer himself, who dedicated it "Al amigo Cesar H. Colombo" (To the friend Cesar H. Colombo). It has the odd subtitle "Canto de dos ruiseñores" (A song of two nightingales) and the classification of "tango criollo." A footnote on the cover warns that any sample that does not have the author's signature should be considered a falsification.
Alarcon, director of the national theater orchestra, enjoyed using many italianisms when indicating how to express the music; on this piece one can see words such as "expressivo", "legatissmo", "scelti", "ben ritmato", etc.
For more information: http://www.todotango.com/
 "El Club Z" (1908)
"El Club Z" (1908)
Composer: Anselmo Rosendo Mendizabal
Performed by: Orquesta del Teatro Apolo Dir: Enrique Cheli
The "Z Club" was composed of a group of revelers headed by Esteban Banza and J. Guidobono. This was an exclusive group formed by forty individuals with the sole purpose of organizing a monthly dance for its members. This group existed from the end of the nineteenth century to the first decade of the twentieth century. The dances were generally held in the house of Maria La Vasca, and it was rented for the entire night for 3 pesos per hour per person. The Afro-Argentine pianist and composer Mendizabal was the usual musician, both as a soloist as well as when he played with his band, which was composed of two violins, a flute, a piano and two guitars. Mendizabal composed many tangos including "El Club Z" where an instrumental call and response surmounts a habanera accompaniment.
Due to prejudices of the time, Mendizabal signed his tangos with the pseudonym "A. Rosendo". The original score included in this anthology is edited by the author by the musical press Ortelli Hnos. Has the dedication, "A los distinguidos socios del Z Club" (To the distinguished members of the Z Club).
For more information: http://www.todotango.com/english/crea...
 “El Pechador” (1909)
“El Pechador” (1909)
Composed by: Angel Gregorio Villoldo
Performed by: Linda Thelma (canto) y Arturo de Siano (piano)
Edited by the house David Poggi e Hijo, it was dedicated by Villoldo “Al celebrado autor nacional don Nemesio Trejo” (to the celebrated national author Mr. Nemesio Trejo), who was the singer and author of comic sketches (1862-1916); it was a popular tango in its time and it was also recorded by Alfredo Gobbi.
Like most, if not all, of Villoldo’s lyrics they are written in the first person and exalt the virtues of the compadrito. Although it may seem inappropriate this title is sung by a woman, the singer Linda Thelma, who has deep roots in Spanish tiples [I have no idea what this is]. She was accompanied on many an occasion by Villoldo himself while recording. Arturo de Siano, a musician who plays with Linda Thelma in this version, was a prominent musician in the theater.
More info on Angel Gregorio Villoldo: http://www.todotango.com/english/creadores/avilloldo.html
More info on Linda Thelma: http://www.todotango.com/english/creadores/lthelma.asp
 “El Purrete (The Kid)” (1909)
“El Purrete (The Kid)” (1909)
Composed by: Jose Luis Roncallo
Performed by: Banda de la Policía de Beunos Aires Dir: Mtro. A Rivara
Basically, all bands incorporated tangos into their repertoires during the first two decades of the century. You can hear the habanera being heavily dramatized as the cymbals clash during the song. These types of bands reached their peak during these years as is demonstrated by the elevated number of recordings made. Some of the most well-known ones include: the 1st Infantry Regiment, the 5th Infantry regiment, the Atlanta, and the Buenos Aires Police.
 “El Purrete”, edited by Breyer Hnos. and dedicated to “El Senor Eduardo Oliveri” (Mr. Eduardo Oliveri) was the first tango written by this author. His style was methodical and consistent with a musician trained in a conservatory. According to unverified claims, the song dates from 1901 and the score dates from some time after, 1903 to 1904.
“El Purrete”, edited by Breyer Hnos. and dedicated to “El Senor Eduardo Oliveri” (Mr. Eduardo Oliveri) was the first tango written by this author. His style was methodical and consistent with a musician trained in a conservatory. According to unverified claims, the song dates from 1901 and the score dates from some time after, 1903 to 1904.
“La Bicicleta” (1909)
Composer: Angel Gregorio Villoldo
Performed by: Angel Villoldo (canto y castañuelas) y Manuel O. Campoamor (piano)
The primitive form of singable rioplatense tango suffered great influences from Spanish zarzuela tango. This is very clearly detectable in the version of “La bicicleta” by Angel G. Villoldo. It has a piano accompaniment by Manuel O. Campoamor purely for melodic purposes as well as castanets played by Villoldo.
Cycling and pelota vasca were the favorite sports during 1895 and 1910, where one could find extensive bicycle caravans traveling to be exhibited in the forests of Palmero after first riding in the city center.
According to Robert Farris Thompson, "Villoldo's 'La bicicleta' (The Bicycle) of 1909 began, nobly, to mix cultures. From the famus black payador Gabino Ezeiza, Villoldo borrows jump-cuts from singing to speech. He hits certain words, like damas and ramas, with flamencolike trills, Arabized melismas that add savor to rhyme. And while he's singing, Villoldo plays castanets!"
More info on Villoldo: http://www.todotango.com/english/creadores/avilloldo.html
More info on Campoamor: http://www.todotango.com/english/crea...
“El Porteñito” (1909)
Composer: Angel Gregorio Villoldo
Performed by: Andrée Vivianne (canto) y orquesta
More info on Villoldo: http://www.todotango.com/english/creadores/avilloldo.html
 “Gran Hotel Victoria” (1910)
“Gran Hotel Victoria” (1910)
Composer: Feliciano Latasa
Performed by: Estudiantina Centenario (trio de bandurrias y guitarra) Dir: Vicente Abad
For more information: http://www.todotango.com/english/biblioteca/cronicas/leyenda_Hotel_Victoria.asp
"Joaquina" (1911)
Composer: Juan Bergamino
Performed by: Manuel O. Campoamor (solo piano)
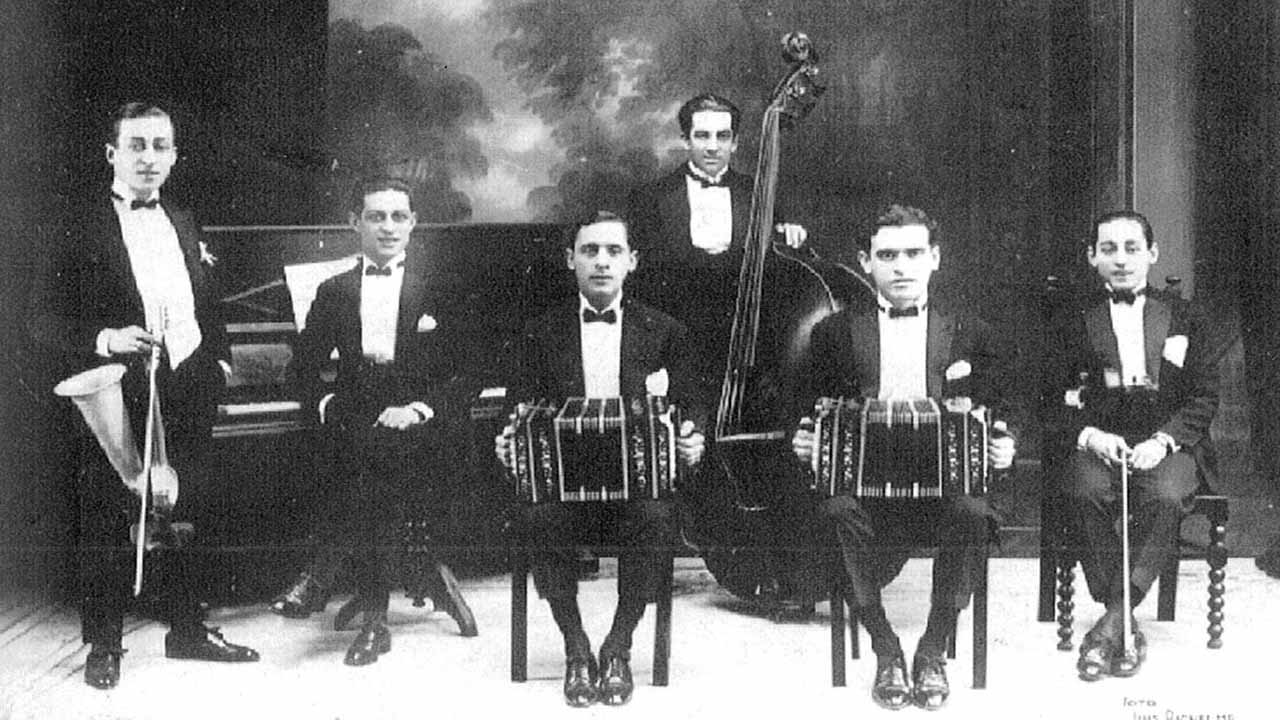



 Julio de Caro
Julio de Caro Tangos were also a popular subject for films and the tango stars of the day, including Gardel, often starred or made appearances in them.
Tangos were also a popular subject for films and the tango stars of the day, including Gardel, often starred or made appearances in them.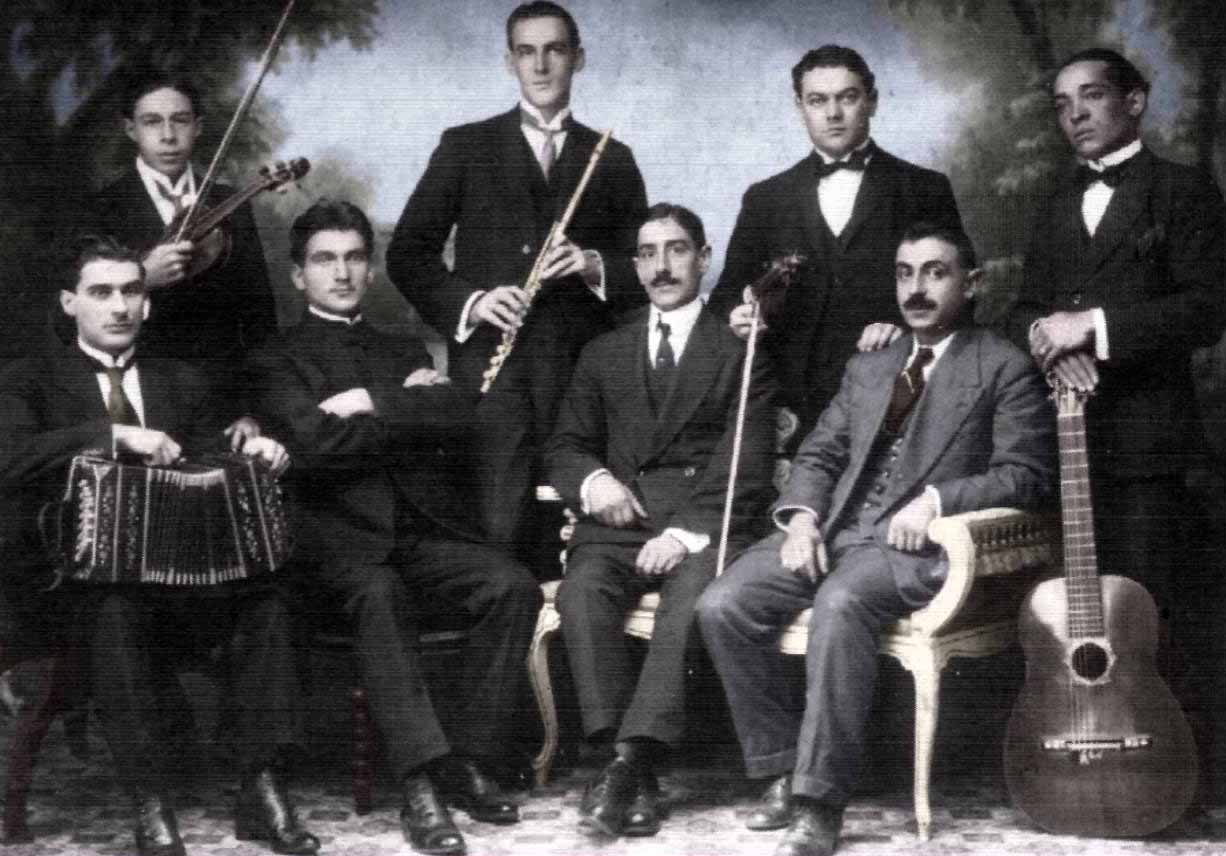
 Orquesta Tîpicas
Orquesta Tîpicas In 1920, the first tango written as a song, "Milonguita." Up until that time, tangos had been written as music first and then lyrics added later. This was the first time that a song was written as lyrics first. It was turned into a movie in 1922 and was the first to feature the theme of the poor, country girl who leaves home to go to the big city of Buenos Aires and becomes a prostitute.
In 1920, the first tango written as a song, "Milonguita." Up until that time, tangos had been written as music first and then lyrics added later. This was the first time that a song was written as lyrics first. It was turned into a movie in 1922 and was the first to feature the theme of the poor, country girl who leaves home to go to the big city of Buenos Aires and becomes a prostitute. Paquita Bernardo was the first professional female bandoneon player and Carlos Gardel said she was, "the only woman who has mastered the macho character of the bandoneon." The debuted her sextet in 1921. There were many women's orquestas and they were popular between 1920 and into the early 1930s. They often played in confiterías, cafés, bars, for weddings and parties. To the best of my knowledge, no women's Orquesta was ever recorded, but there is some film footage of one from the 1933 film, "Tango!"
Paquita Bernardo was the first professional female bandoneon player and Carlos Gardel said she was, "the only woman who has mastered the macho character of the bandoneon." The debuted her sextet in 1921. There were many women's orquestas and they were popular between 1920 and into the early 1930s. They often played in confiterías, cafés, bars, for weddings and parties. To the best of my knowledge, no women's Orquesta was ever recorded, but there is some film footage of one from the 1933 film, "Tango!" “Cara Sucia” (1917)
“Cara Sucia” (1917)

 Pugliese was outspoken in his political opinions and was a communist. These sympathies often brought him into conflict with the government and police. His orchestra was banned from being played on the radio on several occasions. In 1955, Perón had him jailed for six months. He was also jailed by the previous government and later governments. Whenever he was arrested his band would place a red carnation or rose on his piano as a "symbol of absence (símbolo de ausencia)." He was threatened many times during the dark days of the Proceso (1976 to 1983) but as Juan Carlos Copes explains, "he was simply too popular" to "disappear."
Pugliese was outspoken in his political opinions and was a communist. These sympathies often brought him into conflict with the government and police. His orchestra was banned from being played on the radio on several occasions. In 1955, Perón had him jailed for six months. He was also jailed by the previous government and later governments. Whenever he was arrested his band would place a red carnation or rose on his piano as a "symbol of absence (símbolo de ausencia)." He was threatened many times during the dark days of the Proceso (1976 to 1983) but as Juan Carlos Copes explains, "he was simply too popular" to "disappear."
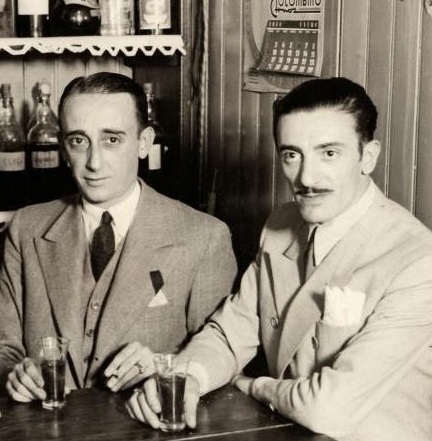
 The Basics
The Basics In 1928, his orchestra was playing at the Florida Cabaret. They had replaced Osvaldo Fresedo's orchestra and it is here that the famous announcer, Príncipe Cubano (The Cuban Prince) (pictured left), anointed d'Arienzo "El Rey del Compás (The King of the Beat)." As d'Arienzo explained it,
In 1928, his orchestra was playing at the Florida Cabaret. They had replaced Osvaldo Fresedo's orchestra and it is here that the famous announcer, Príncipe Cubano (The Cuban Prince) (pictured left), anointed d'Arienzo "El Rey del Compás (The King of the Beat)." As d'Arienzo explained it,  In 1928, he recorded for the first time with his own orchestra, Juan D'Arienzo y Los Siete Ases del Tango. They recorded 44 sides, with the estribillistas: Carlos Dante, Francisco Fiorentino, and, the female singer, Raquel Notar. Other notable members of the orchestra were Ciriaco Ortiz (bandoneon) and Luis Visca (piano). The beat that Príncipe Cubano was commenting on was evident in these recordings and was a return to the beat of the Guardia Vieja period, which many orchestras had abandoned. The beat of the Guardia Vieja movement had a strong driving staccato dance rhythm, D'arienzo's adherence to this would place him in the Canaro school of tango.
In 1928, he recorded for the first time with his own orchestra, Juan D'Arienzo y Los Siete Ases del Tango. They recorded 44 sides, with the estribillistas: Carlos Dante, Francisco Fiorentino, and, the female singer, Raquel Notar. Other notable members of the orchestra were Ciriaco Ortiz (bandoneon) and Luis Visca (piano). The beat that Príncipe Cubano was commenting on was evident in these recordings and was a return to the beat of the Guardia Vieja period, which many orchestras had abandoned. The beat of the Guardia Vieja movement had a strong driving staccato dance rhythm, D'arienzo's adherence to this would place him in the Canaro school of tango. The Tango Cancíon and Guardia Nueva Movements
The Tango Cancíon and Guardia Nueva Movements

 By 1938, d"Arienzo's orchestra was at the height of its popularity. He was just 35 years old, one less than Julio de Caro, but stylistically at the other end of the musical spectrum of tango. His records were selling and they were regularly playing on radio shows. But remember, above, when I made the joke about d'Arienzo being modest? Well, audiences had been becoming bigger and bigger fans of Biagi, and at a concert later that year, after a performance of “Lágrimas and Sonrisas,” the audience clapped until Biagi finally stood up and took a bow. As the story goes, d'Arienzo walked over to him and said, “I’m the only star of this orchestra. You’re fired.”
By 1938, d"Arienzo's orchestra was at the height of its popularity. He was just 35 years old, one less than Julio de Caro, but stylistically at the other end of the musical spectrum of tango. His records were selling and they were regularly playing on radio shows. But remember, above, when I made the joke about d'Arienzo being modest? Well, audiences had been becoming bigger and bigger fans of Biagi, and at a concert later that year, after a performance of “Lágrimas and Sonrisas,” the audience clapped until Biagi finally stood up and took a bow. As the story goes, d'Arienzo walked over to him and said, “I’m the only star of this orchestra. You’re fired.”
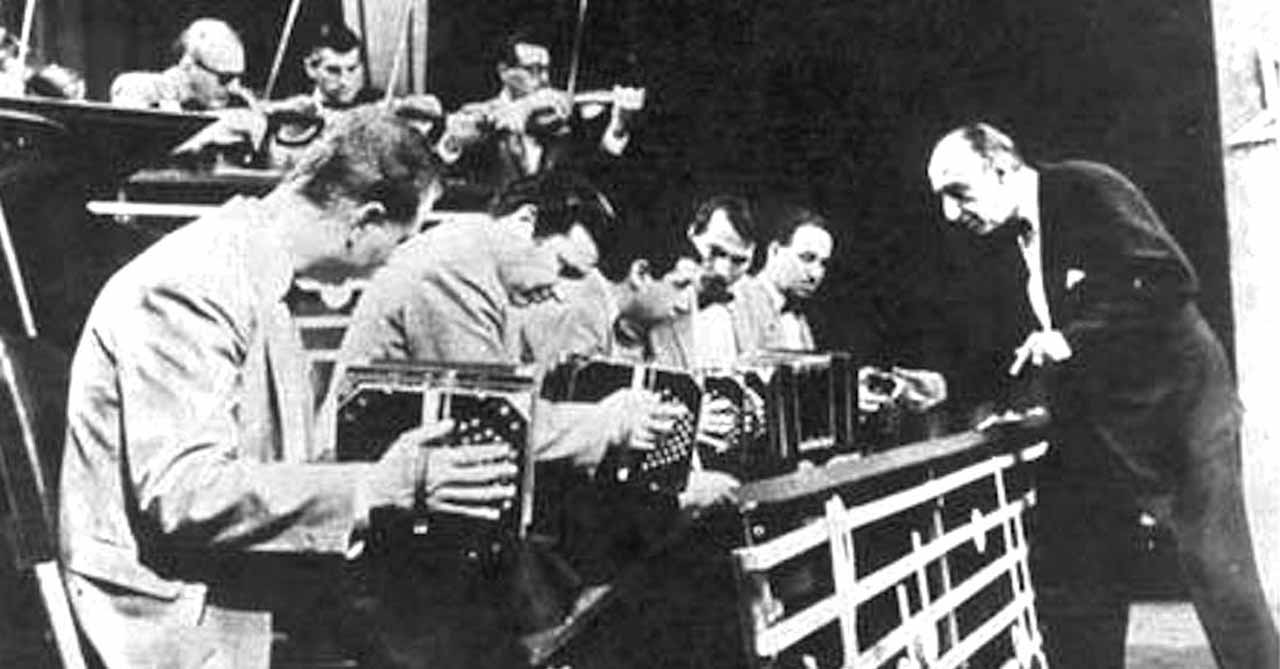


 In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the whole world had been in an economic slump and this included Argentina. But in 1935 Buenos Aires was preparing for the 400th anniversary if its founding as a city. This included building of a 72-meter high Obelisk and the opening of the avenida 9 de Julio. This brought a new energy and optimism to the city.
In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the whole world had been in an economic slump and this included Argentina. But in 1935 Buenos Aires was preparing for the 400th anniversary if its founding as a city. This included building of a 72-meter high Obelisk and the opening of the avenida 9 de Julio. This brought a new energy and optimism to the city. In 1937, Aníbal Troilo's orchestra debuted with Francisco Fiorentino as the singer. Troilo was a large man and had the nickname "Pichuco." He was an innovator and kept pushing tango into new areas especially once he hired a young bandoneon player named Astor Piazzolla and made him arranger for his orchestra. Troilo was popular with both dancers and the listening public. To this day, his pictures are hanging all over Buenos Aires cafés and restaurants. Listen to his song, "Tinta Roja" below.
In 1937, Aníbal Troilo's orchestra debuted with Francisco Fiorentino as the singer. Troilo was a large man and had the nickname "Pichuco." He was an innovator and kept pushing tango into new areas especially once he hired a young bandoneon player named Astor Piazzolla and made him arranger for his orchestra. Troilo was popular with both dancers and the listening public. To this day, his pictures are hanging all over Buenos Aires cafés and restaurants. Listen to his song, "Tinta Roja" below.